From pharmaceuticals to food processing, fluid bed dryers are revolutionizing drying methods. In numerous industries, the efficient drying of strong materials is crucial for maintaining great product, decreasing manufacturing expenses, and ensuring the highest quality method manipulation. Among the huge range of drying strategies to be had, fluid bed dryers have gained massive popularity due to their versatility, power performance, and advanced drying performance. This complete manual targets to:
Most dryers use hot air as a drying medium. Dryer designs differ in how the hot air and wet material to be dried interact in the drying equipment. In a fluid bed dryer, the solid particles are suspended in a current of air that is fast enough to make the particles float in the air. A fluid bed dryer is usually some form of metal box with a horizontal perforated plate mounted in it.
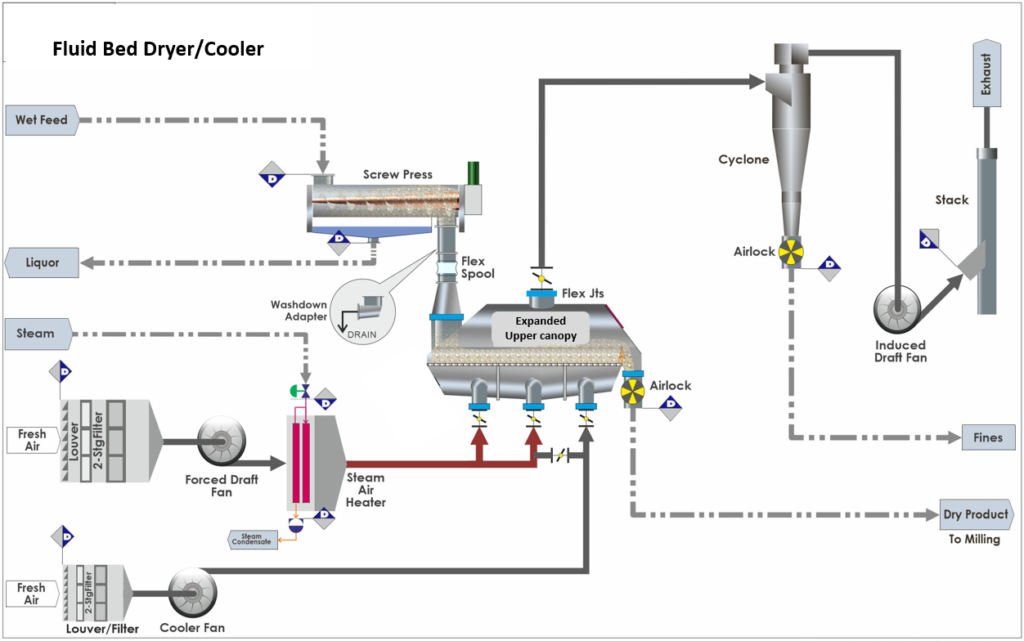

In the world of industrial drying, fluid bed dryers have emerged as highly efficient and versatile systems. Their working principle based on fluidization allows for smooth and uniform drying of solids. In order to optimize drying processes across industries, it is important to understand the basic principles behind them. So, this section of our article will delve into the operating principle of fluid bed dryers, highlighting the key stages and mechanisms involved.
In the core of the fluidized bed dryer lies the concept of fluidization. Fluidization happens when a gas, usually air, passes through a bed of solid particles from below. As the air current gets faster the particles are lifted into the air stream so that there is a mixture of separate particles suspended in the air stream this causes the bed of particles to expand and act like a fluid. There is a range of velocities over which the particles will fluidise. This is called the fluidising velocity.
The fluid bed drying process begins with a heating step. The drying air is heated to the desired temperature using a heater or heat exchanger. The hot gas is then fed into the lower plenum of the dryer by a set of branched ducting fitted with dampers. These can adjust the amount of air which feeds into each part of the dryer inlet air plenum.
A horizontal perforated plate is mounted above the lower air plenum, this distributes the air across the bed of material. The powder which is above the bedplate mixes with the air and this mixture acts like a fluid. Wet powder is fed in at one end of the bed and the height of the fluidized material is maintained by a discharge weir at the other end of the bed where the dried product spills over to the next process.
In the fluidized state, the particles in the bed are surrounded by hot drying air. This mixture provides greater contact between the heated gas and the wet material, facilitating effective heat transfer and evaporation. The gas transfers its heat energy to the solid particles, evaporating the moisture from the material into the air. to be carried out of the dryer in the exhaust.
The lower plenum can be divided into separate sections each with a different drying inlet temperature or fluidising velocity. This allows for higher temperatures to be used at the feed end of the bed where the product is wetter and lower temperatures in subsequent stages as the surface of the particles becomes dryer. If the product has a high moisture content at the feed end of the bed and much lower product moisture then the fluidising velocity will change as the material progresses down the bed. In this case less airflow would be required as the material passes from one stage to the next.
Once the drying process is complete, a controlled flow of cool air may be introduced into a final stage after the drying sections to cool the dried material. This ensures that the product is stable for storage and packaging.
During fluidization, finer particles will be blown off the bulk of the product which is fluidized. The upper canopy of the fluid bed is flared to lower the gas velocity and allow some of the fine particles to fall back into the fluidized material. Some fines are always carried out with the exhaust air to the gas cleaning system. In some processes it is desirable to use the fluid bed to separate fines from the bulk of the material by carrying them away in the exhaust. This is called termed elutriation.
Fluid bed dryers can be classified into different types based on their design and operating principles. However, it’s important to note that fluid bed dryers can have modifications and hybrid designs that are suited to certain applications and requirements. The most appropriate kind is determined by considerations such as the material to be dried, required drying qualities, energy efficiency, and process control requirements.
With that said, the main types of fluid bed dryers include:
Conventional fluid bed dryers have a straightforward design and are frequently used in a variety of industries. They are made out of a perforated bed or plate that holds the material to be dried. The particles fluidize as heated air is supplied from the bed's bottom. After that, the fluidized particles undergo effective heat and mass transmission, resulting in moisture evaporation and drying. Conventional fluid bed dryers are flexible and may be used in various applications.
Vibrating fluid bed dryers use extra vibrating mechanisms to improve fluidization. Vibrations are used in these dryers to promote movement of larger particles or sticky wet agglomerates which cannot be fluidized by the air alone. The vibration can also be used to minimize the fluidizing velocity for materials with a wide particle size distribution so that the larger particles are agitated by the vibration and the finer material by the fluidizing air. This will minimize the loss of fines to the exhaust air. In Dedert’s VFBs, vibration is achieved using out of balance vibratory motors and the fluid bed units are mounted on air springs to isolate them from the support structure.
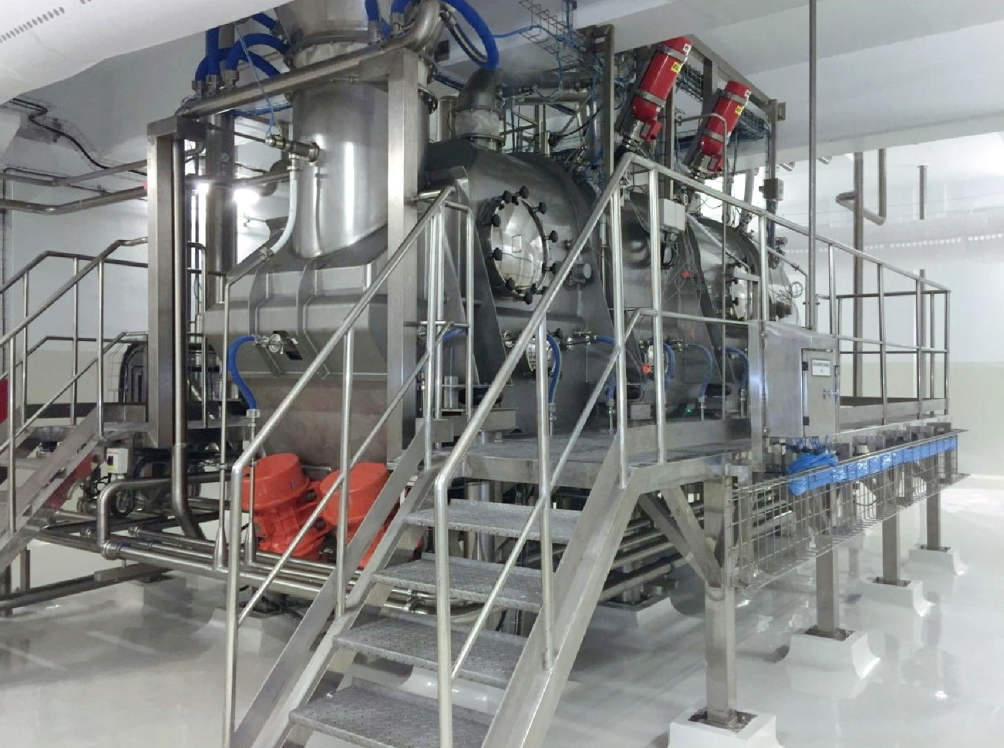


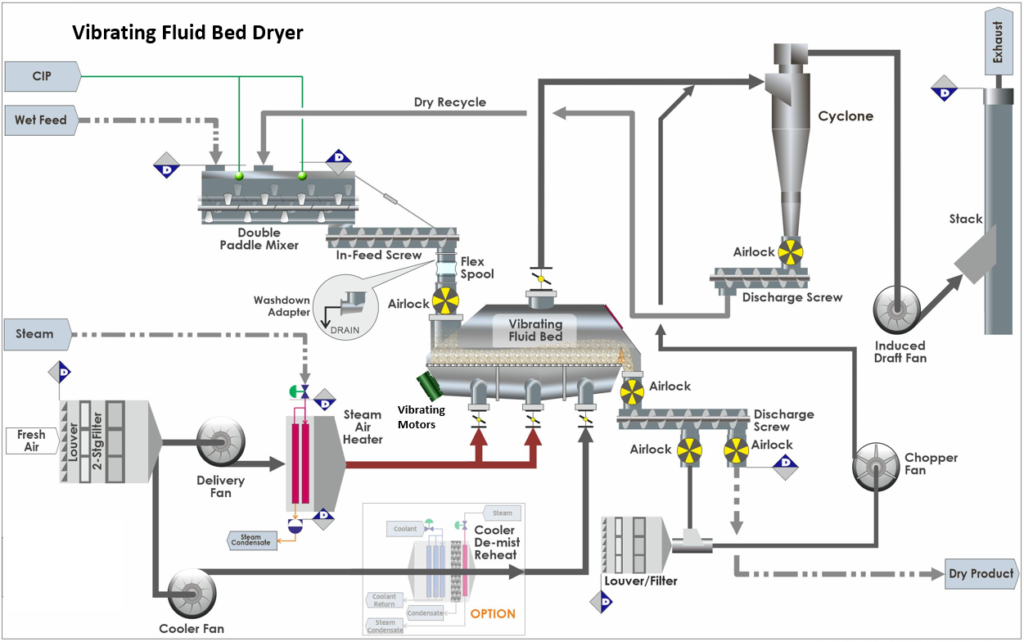

Agitated fluid bed dryers boost drying efficiency by combining fluidization with mechanical agitation. Within the bed, agitators or stirrers continually agitate the particles. This agitation improves heat and mass transport, resulting in faster drying. Agitated fluid bed dryers are ideal for drying materials with poor fluidization qualities or high moisture content and for uniformly drying cohesive materials.
The principal energy loss from a dryer is generally in the exhaust. One way of improving the energy efficiency is to recycle exhaust gas back to the dryer inlet. This has a few effects:
The energy input to the dryer is reduced.
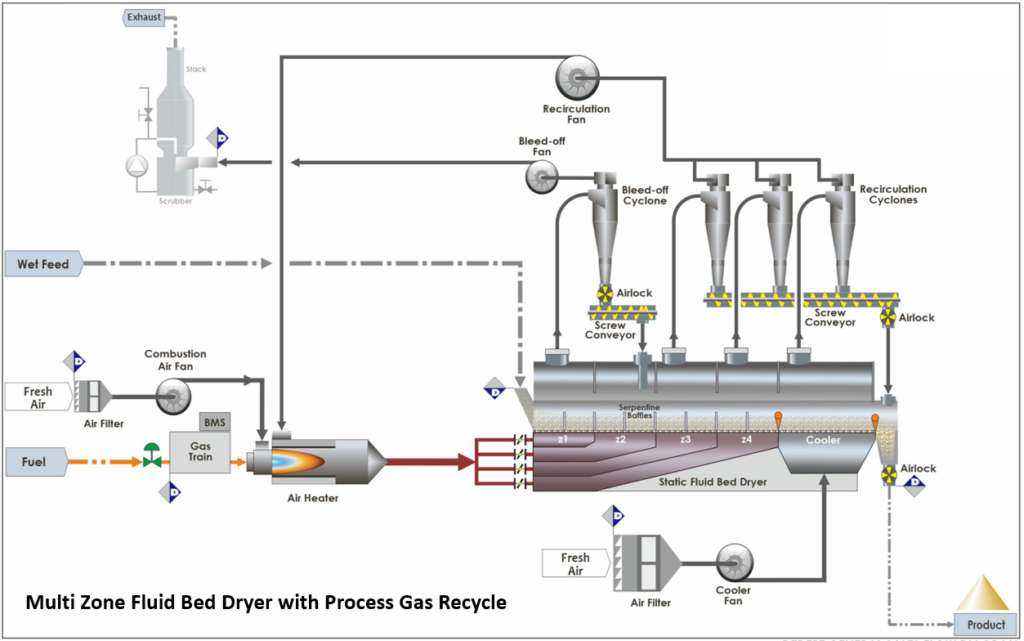

Fluid bed dryers have gained increasing popularity in various industries due to their versatility, efficiency, and drying capacity. These dryers have many applications in agriculture, from pharmaceuticals to food processing and minerals. Let's explore the many applications of fluid bed dryers.
Fluid bed dryers play an important role in the pharmaceutical industry, where accurate drying of pharmaceutical powders, granules, and tablets is important. In fact, it is by far the most widely used dryer in the pharmaceutical industry. The main applications are:
| Drying of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) | FBD ensures uniform slow drying of APIs, maintaining consistent strength and quality. |
| Granulation Drying | After the wet granulation process, an FBD is used to dry the granules. This ensures proper particle size distribution and moisture content. |
| Tablet Drying | FBDs have the capability to effectively remove moisture from tablets without compromising their structural integrity after tablet coating or moisture-sensitive processes. |
As with the pharmaceutical industry, fluid bed dryers find great utility in the chemical industry for drying various chemical compounds. Some common uses are:
| Drying of Chemical Powders | FBDs efficiently dry a wide range of chemical powders, including dyes,pigments,catalysts,and specialty chemicals. |
| Polymer Drying | The polymer processing industry uses FBDs to remove moisture and solvents from polymer pellets, ensuring consistent quality and performance. |
| Chemical Reaction Drying | In some chemical reactions, FBDs are used to remove water or other by-products, which helps in the completion of the reaction. |
Proper drying of food products is essential for quality and shelf life. This is where fluid bed dryers find their usage in the food processing industry.
| Drying Grains and Cereals | FBDs are used to remove moisture from grains, cereals, and seeds to improve product stability and prevent spoilage. |
| Drying Coffee Beans | During processing, coffee beans need a gentle and uniform drying to preserve their flavor and aroma. FBDs can be configured to do just that. |
| Drying of Fruits and Vegetable | FBDs are used to remove moisture from fruits and vegetables before further processing or packaging, thus extending the shelf life. |
Fluid bed dryers find application in the mineral aggregate industry too, for drying and de-agglomerating materials. Key applications include:
| Drying Minerals and Ores | FBDs can effectively remove moisture from minerals and aggregates, enhancing their processing and processing properties. |
| De-agglomeration | In industries where aggregate particles need to be crushed, fluidized bed dryers can provide effective de-aggregation through gentle drying and controlled airflow. |
Fluid bed dryers also have applications in many other industries:
| Drying Biomass | Moisture removal is crucial for efficient combustion in biomass fuel. FBDs are used in their production. |
| Recycling and Waste Management | FBDs help to dry and process various waste materials, which enables their conversion into usable products or fuel sources. |
Fluid bed dryers offer many advantages over other drying methods, making them desirable in many industries. Some key advantages include:
| Rapid and Uniform Drying | The fluidization process ensures excellent heat and mass transfer between the gas and the particles. This results in efficient moisture removal and consistent drying throughout the bed. |
| Gentle Handling | The fluid-like behavior of particles minimizes the risk of material degradation or damage. The gentle handling capability is particularly important for delicate or sensitive materials, such as pharmaceutical powders or fragile food ingredients. |
| Energy Efficiency | Compared to other drying methods, they consume less energy due to shorter drying times and efficient heat transfer. The direct contact between the drying gas and the particles enables quick moisture evaporation. |
| Easy Scale-up | These dryers are easily scalable from laboratory-scale to large industrial units. This allows for seamless process optimization and adaptation to changing production requirements. It also facilitates technology transfer from R&D to commercial production. |
| Versatility | FBDs can handle a wide range of materials with different particle sizes, shapes, and properties. By adjusting the fluidization parameters, such as airflow rate and temperature, FBDs can accommodate various materials, making them versatile for different applications and industries. |
| Enhanced Product Quality | The controlled drying conditions help maintain the integrity, color, flavor, and other quality attributes of the dried products. The uniform and efficient drying process ensures consistent product quality and reduces the risk of over-drying or under-drying. |
Choosing the right fluid bed dryer is important for optimal drying processes and achieving the desired results in various industries. With so many options available, it is important to consider various factors to ensure that the dryer selected will meet specific requirements.
Particle size and shape affect the fluidization behavior and drying kinetics. To guarantee efficient fluidization and drying, the dryer must be capable of accepting specified particle properties.
The initial moisture content influences drying time and drying factors. It is critical to select a fluid bed dryer that can successfully remove the necessary moisture content in the timeframe specified.
Some materials are susceptible to high heat and must be dried at lower temperature to avoid deterioration. In such instances, it is critical to pick a fluid bed drier with accurate temperature control.
Determine the necessary drying capacity in terms of material weight or volume processed per unit of time. Ensure that the dryer you choose can satisfy your production needs without sacrificing drying efficiency.
The time necessary for full drying varies according to the material. Choose a fluid bed dryer with enough residence time to enable proper moisture removal without the risk of over or under-drying.
Assess the heating method's energy efficiency and compatibility with the available energy sources. Choose a heating method that strikes a balance between energy usage and drying efficiency.
Assess the heating method's capacity for accurate temperature control. Temperature regulation is crucial for preserving product quality and avoiding overheating or underheating.
Analyze the capabilities of the control system to monitor and alter drying parameters such as temperature, airflow rate, and humidity. Look for extensive control options as well as easy-to-use interfaces.
Consider possibilities for automation, such as programmed recipes, data logging, and remote monitoring. Automation improves process control, decreases human mistakes, and simplifies processes.
Make sure that the materials used in the dryer's construction are appropriate for the purpose, such as stainless steel for the pharmaceutical or food processing sectors.
Take a look at the ease of access for cleaning and maintenance. Look for features that make cleaning easier and faster, such as detachable parts and easy-to-clean surfaces.
To ensure product quality and limit contamination concerns, consider the design of the air handling system, including filtering and exhaust systems.
Fluid bed dryers have become incredibly popular across industries for their versatility, energy efficiency, and superior drying performance. Their versatility, energy efficiency, and ability to maintain product quality make them a valuable choice for various industries. But remember, choosing the right equipment is only half the battle. If you know the proper operating and maintenance procedures of these behemoths, they will keep running like new for years to come. Dedert’s decades of expertise can provide you with invaluable assistance in this regard.
©2024 Dedert Corporation. All Rights Reserved.